
Every diamond has its own unique characteristics. The 4Cs — Color, Clarity, Cut, and Carat weight —are the internationally acknowledged standards for determining a diamond's quality.
The ‘Cut’ is the most quintessential characteristic of a diamond quality that impacts a diamond’s exquisiteness. Diamond-Cut especially relates to the quality of a diamond’s angles, proportions, symmetrical facets, brilliance, fire, scintillation, and finishing details. Also, more than any other aspect, the cut determines the beauty of the stone & add value to diamond jewelry.
The ideal and excellent grades, as per the diamond shape, shows symmetries, and angles cut for maximum brilliance and fire. The GIA diamond cut chart grades diamond cut on the scale of
Ideal - Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair, and Poor.
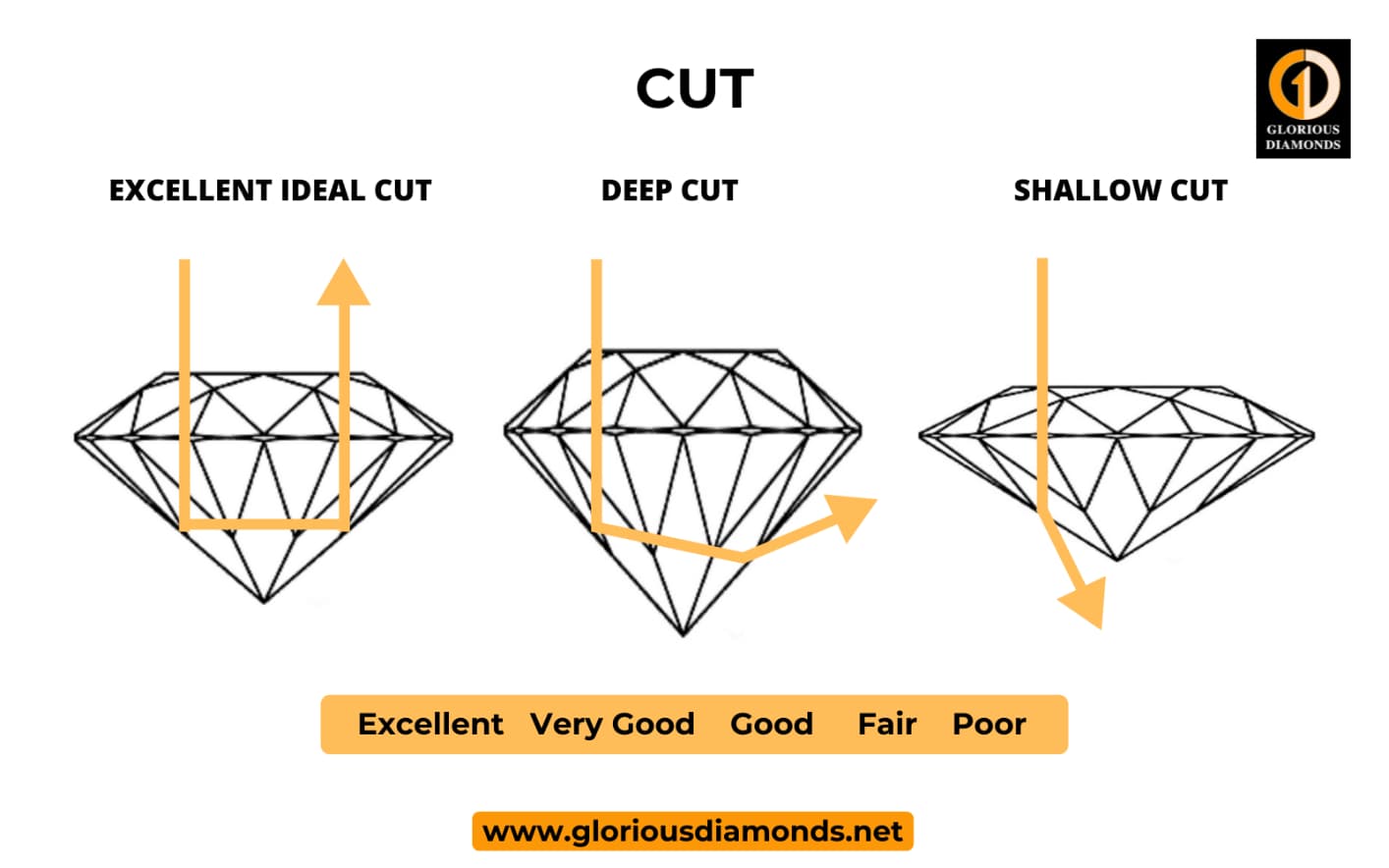
GIA DIAMOND CUT GRADE CHART
A professional gemologist at the GIA reviews each diamond under magnification to determine the Cut grade. Here are the GIA diamonds cut grades:
| Excellent | Excellent Cut Diamonds have even more fire and luster of any diamond | |
|---|---|---|
| Very Good | Very Good Cut Diamonds are known for their brightness and fire. Very Good diamonds appear to sparkle similarly to Excellent diamonds with naked eye | |
| Good | Good Cut Diamonds represents brilliance and sparkle, with much of the light reflecting through the table to the viewer’s eye. | |
| Fair | Light easily departs through the bottom and sides of a fair cut diamond, resulting in minimal brilliance. | |
| Poor | Poor cut diamonds have almost no radiance, brilliance, or fire. | |
Diamond Cut
The Diamond Cut Grade is based on the overall proportions, symmetry, and polish of a diamond. The cutter must achieve the proper balance of all these factors in order to produce a stone that will perform optimally in terms of both its beauty and its ability to return light back to the viewer.
When evaluating the cut of a diamond, the GIA takes into account:
Why Choose a GIA Certified Diamond?
There are many reasons to choose a GIA diamond. This means that you can be confident you are getting the best possible value for your money when you purchase a GIA-certified diamond. certified diamond, but the two most important are quality and value.
GIA-certified diamonds are simply the best quality diamonds available on the market. They are cut to precise standards and have been evaluated for their beauty and light performance by the most experienced gemologists in the world.
In addition, because GIA-certified diamonds are so well-respected, they often sell for a premium over non-certified.
The Science Behind Diamond Cutting
The art of diamond cutting is both an art and a science. The cutter must take into account the weight, symmetry, and proportions of the stone in order to create a diamond that is not only beautiful but also performs optimally in terms of light return.
GIA-certified diamonds are cut to precise standards that ensure they will deliver the maximum amount of light return. This means that they will appear brighter and more sparkly than non-certified diamonds.
When you purchase a GIA-certified diamond, you can be confident that you are getting a high-quality, well-cut diamond that will perform beautifully for years to come.
How a Diamond’s Cut is Graded
The GIA grades diamonds on a scale from Excellent to Poor. The vast majority of diamonds fall into the Good, Very Good, or Excellent categories. Only a small percentage of diamonds are graded as Poor. These diamonds have been cut so poorly that they have lost a significant amount of their original weight and do not perform well in terms of light return. When you purchase a GIA-certified diamond, you can be confident that you are getting a high-quality, well-cut diamond.
Summary of Diamond Cut
In summary, the cut of a diamond is very important. It affects the diamond's beauty and light performance. GIA-certified diamonds are cut to precise standards that ensure they will deliver the maximum amount of light return. This means that they will appear brighter and more sparkly than non-certified diamonds. When you purchase a GIA-certified diamond, you can be confident that you are getting a high-quality, well-cut diamond.
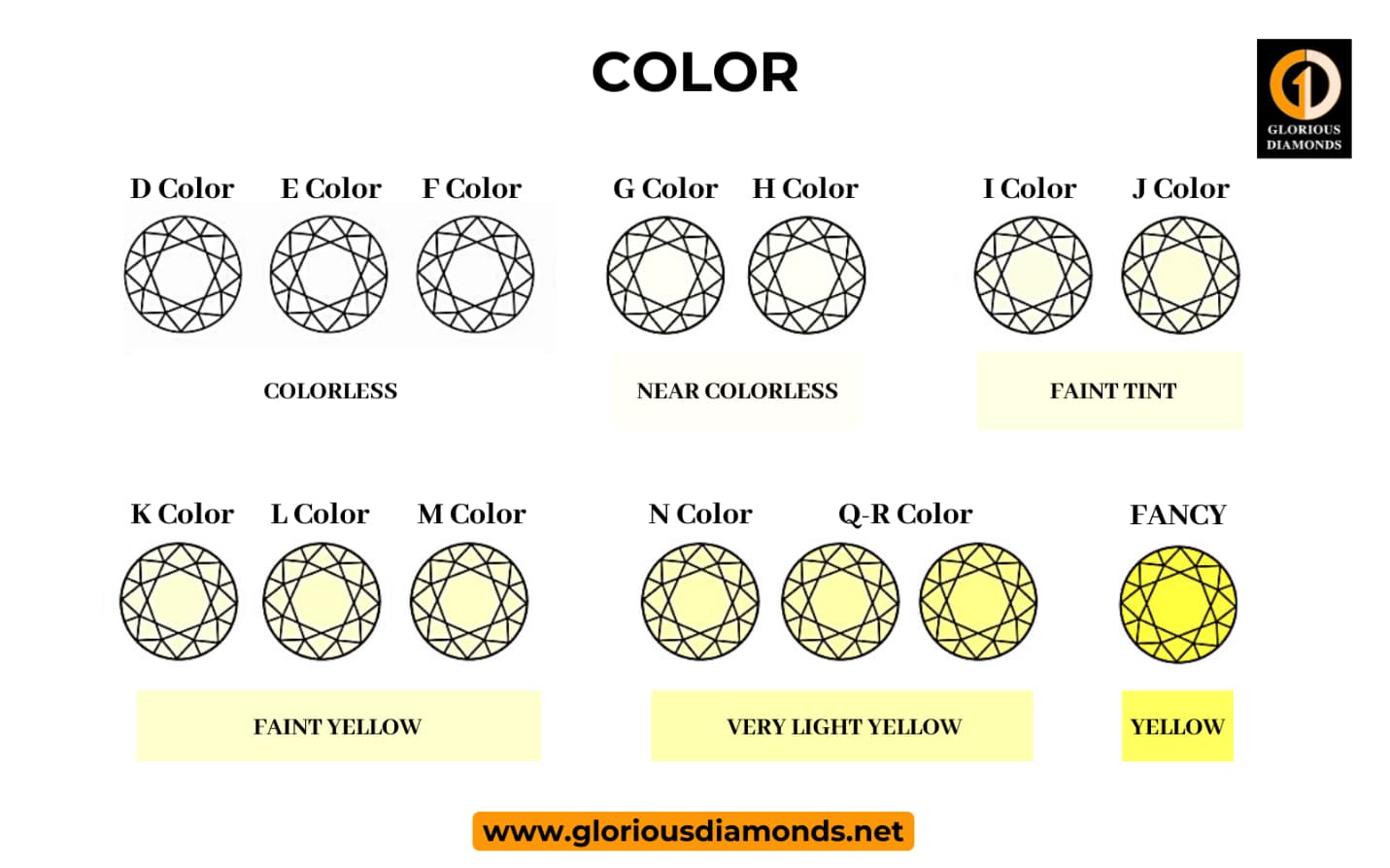
The GIA color-grading system for diamonds starts with the letter D, which stands for colorless, and progresses to the letter Z, which stands for pale yellow or brown. The color appearance of each letter grade is well specified. Under regulated lighting and precise viewing conditions, diamonds are color-graded by comparing them to stones of known color.
| D | The highest color grade is D, meaning it has nearly no color. D color diamond appears colorless under magnification and to the naked eye. | |
|---|---|---|
| E | An E color is the second-best color of diamond colors. E color diamonds look almost similar to D color diamonds. Sitting squarely in the middle of the elite “colorless” range (DEF), this particular color grade is virtually indistinguishable from perfectly colorless. | |
| F | An F color diamond is high on diamond color scale, known as “colorless” by gemologists which includes D, E and F colors. There are only 2 color grades higher than F color, while there are 20 grades lower than an F color diamond. F color is almost identical to D and E color diamonds, with nearly no visible color. | |
| G |
The G color grading is the highest & best grade in the “Near Colorless” range of the GIA’s scale, which includes diamonds graded G to J. G color diamonds have some tints of color, although they’re almost impossible to see with the naked eye. |
|
| H | The GIA's color scale places H color diamonds in the "near-colorless" category. They appear nearly colorless, but when seen under magnification by an expert gemologist, they may display a little yellow tint. | |
| I | The I color grade is the second-lowest in the near-colorless range. Diamonds with the I color are ones that are in the middle of the Near Colorless category. I color however, lower range of white but not too yellow. | |
| J | J color diamonds appear colorless to the naked eye, but have a slight yellow tint that is visible under bright lights and magnifying glass. J color diamonds can be excellent choice in terms of value for money. | |
| K - L - M | On the GIA's diamond color scale, K-L-M color diamonds are classified as "faint tint," K-L-M colors are simply a "breakpoint" between near colorless and faint yellow. Which means they have a slight yellow tint that may be seen with the naked eye. | |
| N - R | Diamonds in the N to R category have easily noticeable yellow or brown tinting. These diamonds are available at a much lower price point than faintly tinted or near colorless diamonds. | |
| S- Z | Diamonds of an S-Z range is very close to fancy color diamonds. | |
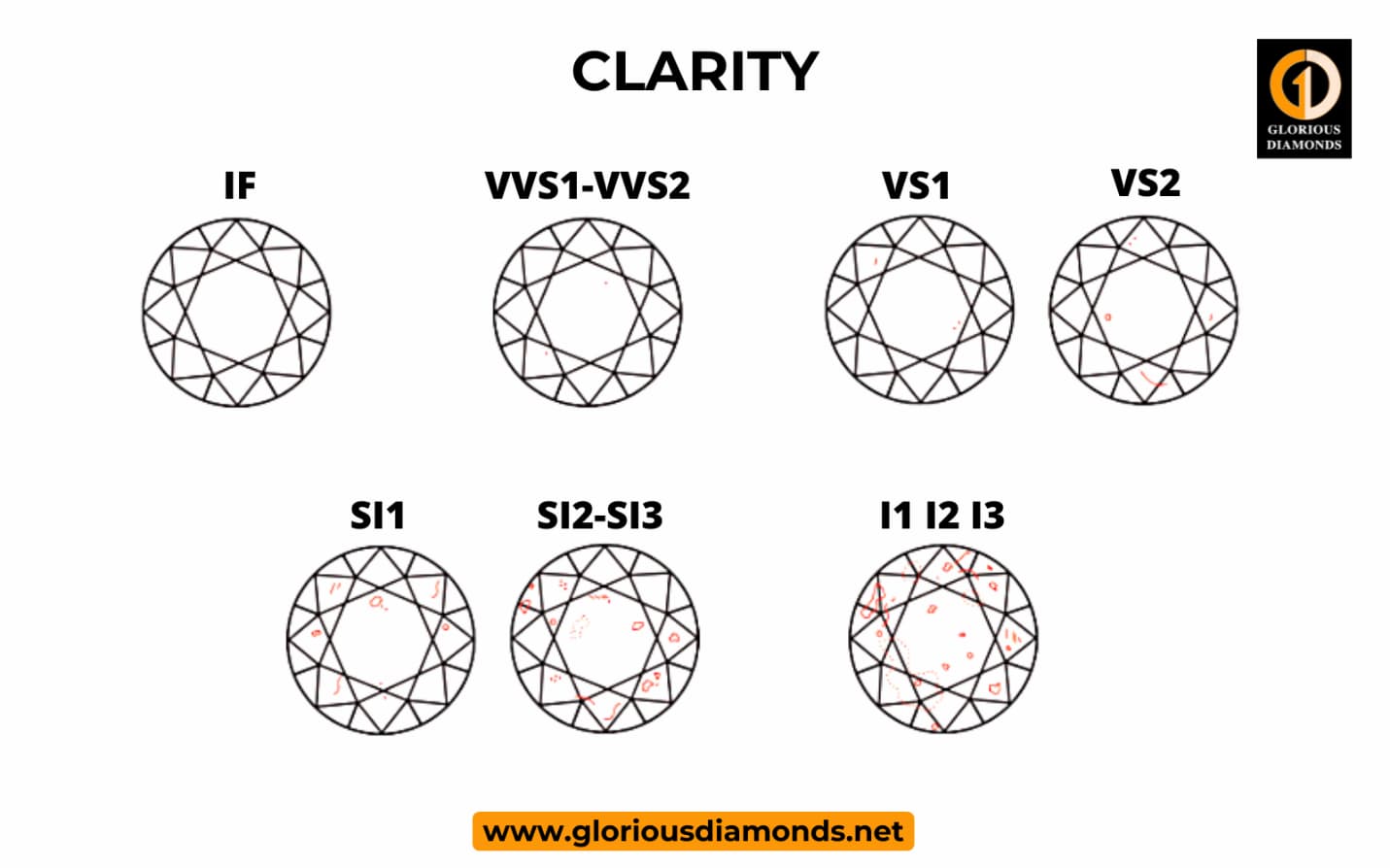
Diamond clarity refers to the presence and visual appearance of internal characteristics of a diamond known as inclusions, as well as surface defects known as blemishes. One of the 4Cs of grading is clarity.
Diamonds with higher clarity grades are more valuable, with the extremely rare "Flawless" graded diamond commanding the highest price.
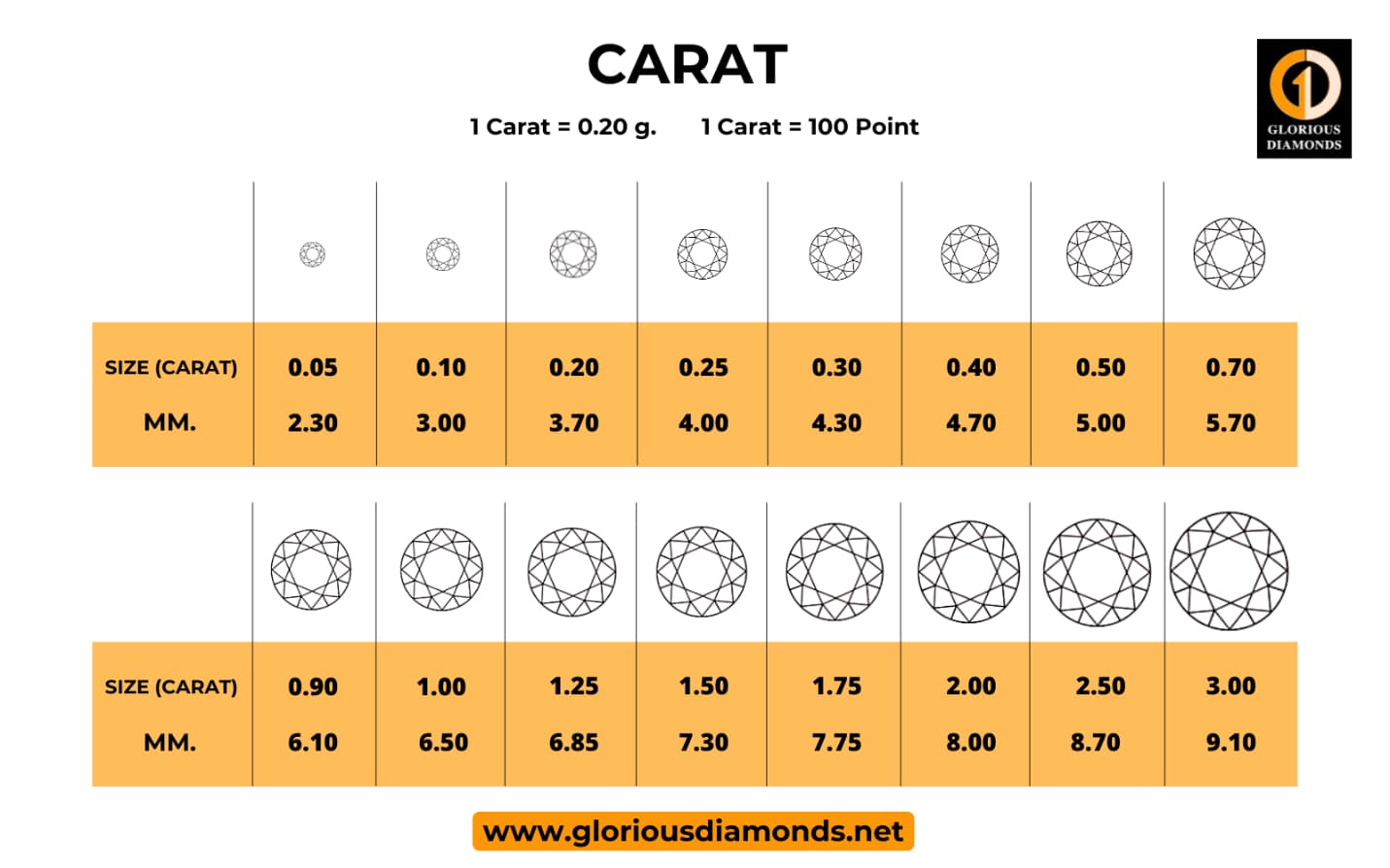
Diamond clarity refers to the presence and visual appearance of internal characteristics of a diamond known as inclusions, as well as surface defects known as blemishes. One of the 4Cs of grading is clarity.
The carat weight of a diamond is used to determine its size. Because one carat is divided into 100 points, a diamond weighing 75 points weighs 0.75 carat. As larger diamonds are rarer and more valuable, their price rises with their carat weight.
“Glorious Diamonds” We are diamond factory & Diamond shop online , Our diamond jewelry from the best-cut sources, With a GIA quality guarantee.
Our products / services
Diamond Education
Diamond Price
GIA Certificate & Diamond Characteristics
Contact Us
919/503-504, 43rd floor,
Jewelry Trade Center Building,
Silom Road, Kwaeng Silom, Khet Bangrak
Bangkok 10500 Thailand
Customer Service +669 421 99999
+669 469 09000
Office +6626302728
Email sales@gloriousdiamonds.net






